
Marketing researcher and educator at Ahrefs. Mateusz has over 10 years of experience in marketing gained in agencies, SaaS and hardware businesses. When not writing, he's composing music or enjoying long walks.
Article Performance Data from Ahrefs Linking websites Get SEO metrics of any website or URL.The number of websites linking to this post.
This post's estimated monthly organic search traffic.
Get the week's best marketing contentMarket research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
In other words, it’s the process of understanding who your business is targeting so you can better position your marketing strategy.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
A marketing strategy is a business’s overall game plan for reaching consumers and turning them into customers.
The key word in the above definition is “game plan”. Entering a market with a product is like starting a new game. Since you’re new to the game, you don’t know the rules, and you don’t know who you’re playing against.
This is exactly where market research comes in. Market research allows you to discover the rules of the marketing game by understanding your target audience. Moreover, it allows you to understand who your opponent is by assessing the strengths and weaknesses of your competition.
Research is what marketing pros do to plan their moves, and outperform their competition. It’s also what marketing pros use to identify the strengths and weaknesses of their own marketing strategy.
But is market research the ultimate business oracle? Unfortunately no. Even companies that specialize in market research admit it - here’s a quote from one of them:
(…) it cannot be assumed that market research is an exact science, as it would be unrealistic and unreasonable to expect market researchers to predict the precise demand for a new concept, given that there are numerous variables that can impact demand outside of the market researchers’ remit.
That’s why market research with all of its significance is “only” a part of marketing, and it’s “only” an experiment. It’s up to you whether you will conduct your experiment, and when you will end it.
For example, Crystal Pepsi seemed very promising in the market research phase, yet it failed when released onto the market (a similar thing happened to New Coke). Xerox’s idea for a commercial photocopier was a no-go in the eyes of research analysts; Xerox did it anyway, and the rest is history.
Paul N. Hauge and Peter Jackson in their book “Do Your Own Market Research” point to three specific situations when market research is really useful:
Another answer to the “when” is the importance of the decision that you need to make. The more important the marketing issue you’re tackling, the more market research comes in handy.
For example, launching a new car on the market is quite a big event, right? So maybe Ford could have avoided losing 350 million dollars with the Ford Edsel if they had done their research properly. I mean, with the right methods in place it shouldn’t be that hard to predict that consumers will deem the car overpriced and ugly.
That said, market research doesn’t always have to be a large, complex project. The relatively new trend of agile market research allows you to research the market regularly and in a cost-effective way. This is where you employ bite-size, iterative, and evolutionary methods to react to fast-changing circumstances and adapt to unknown market territories.
Furthermore, if you’re working in startup conditions, especially if you’re developing an innovative product, you may be interested in customer development. In this methodology market research is at its “agilest” and it’s tightly woven into the product development process.
Take Ahrefs for example. We stick to agile market research hacks anyone can use. As you will see later in the article, we use simple (but effective!) stuff like social media polls, crowdsourcing, in-house competitive analysis, or just tracking the pricing of our competitors.
Case in point, just recently we asked our fellow marketers on Twitter how they go about researching the market. It seems that market research comes in all shapes and sizes:
Have you ever performed “market research?“
What was it for?
— Tim Soulo (@timsoulo) May 3, 2021Just because somebody does market research in a certain way doesn’t mean that you need to copy that. You should know your options, and they start with the different types of market research.
Whenever the research is done by you or on your behalf, and you need to create the data to solve a given problem, that is called primary market research.
Examples: Focus groups, interviews, surveys (more on those later in the article).
Key benefits: It’s specific to your brand and products or services, and you can control the quality of the data.
Whenever you’re using already existing data, such as that put together by other businesses and organizations, you’re doing secondary market research.
Examples: Second-party and third-party sources like articles, whitepapers, reports, industry statistics, already collected internal data.
Key benefits: Get a macro perspective of your marketplace, as secondary research includes other players in the market, and most probably utilizes a bigger set of data than your primary sources.
Primary and secondary market research are different but by no means opposite. It’s actually recommended to use both.
While primary sources will give you a focused, micro perspective of your business, secondary research will tell you how other businesses are doing and how your research findings compare to bigger research sample sizes.
A bit more theory for all you marketing geeks out there. Professional market researchers distinguish between the following primary and secondary market research subtypes:
Let’s go over some popular market research methods you can use yourself and/or outsource.
The data you’ve already collected in your company is an invaluable secondary research data source. The more time you’re in the business, the more data you have on your hands.
The best thing about your internal data is that it’s been put into practice in real-life market conditions, so you just need to find the patterns and draw conclusions.
Here are some internal data sources you can leverage:
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions and are great for exploratory qualitative research.
In unstructured interviews, you have an informal, free-flowing conversation on a given set of topics.
In structured interviews, you prepare a detailed, rigorous interview protocol where you list every question you want to ask and you can’t divert from them.
You can also choose the “middle way” with semi-structured interviews which revolve around predefined themes or questions, but allow for open-ended discussion.
A word of advice here would be to always remain neutral and unbiased, even during unstructured interviews. Also, it’s helpful to perform a pilot test of the interview to quickly spot some defects of your protocol.
Recording the interview may influence the answers, so use it wisely.
Focus groups are where 5 to 10 people with common characteristics take part in an interactive discussion with a moderator. They’re used to learn how a particular group thinks about a given issue or to provide feedback on a product.
Now, you might know that Steve Jobs famously hated focus groups. He’s on record saying:
It’s really hard to design products by focus groups. A lot of times, people don’t know what they want until you show it to them.
If you’re trying to create a leapfrog product like the iPhone, there’s probably some validity to this statement. But most of us aren’t wrestling with that level of ambition. We just want to know if customers will like a proposed new feature or not. For this, focus groups are super useful.
Surveys involve polling your audience. They’re usually performed online for customer satisfaction and loyalty research, and are one of the most popular and cost-effective market research methods.
Some of the tried and tested use cases of online surveys are:
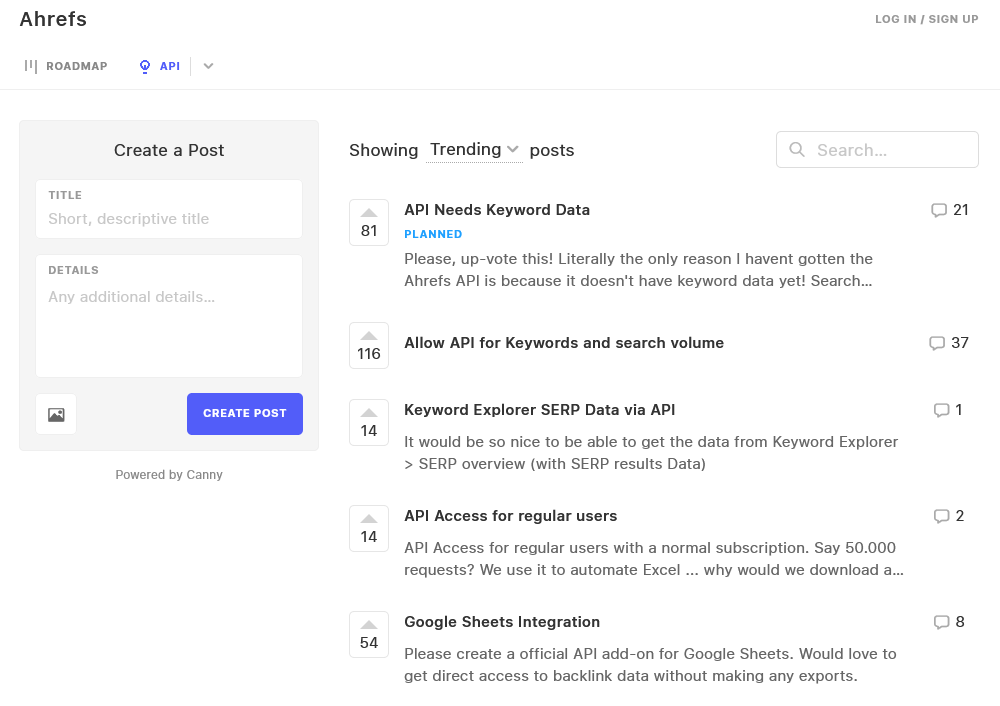
An interesting example of surveying the market is crowdsourcing. That’s what Ahrefs does to understand what features to build, how important they are, and what customers expect from them.
What’s unique about crowdsourcing is that it allows the users to add their own ideas, and upvote or comment on existing ideas rather than answer predetermined questions, so this method leaves less room for marketing myopia. You improve your business, and the users get a better product—everybody wins.

How we crowdsource ideas at Ahrefs
Social media is another great place to survey the marketplace.
How many of you have disavowed links in GSC this year?
— Tim Soulo (@timsoulo) October 8, 2020
Market segmentation is the practice of categorizing a market into homogeneous groups based on specific criteria, also called segmentation variables (like age, sex, company size, country, etc.).
If you think you’re building a product for everyone, think again. Not everyone will want to buy from you.
Smart companies pick their target audience carefully. They pinpoint groups of people or organizations that could be valuable customers for the business. That way they also discover their non-ideal customers and develop a plan to attract customer segments gradually.
Ever wondered why Procter and Gamble creates so many, often competing, brands? You guessed it: market segmentation. P&G simply divides and conquers. Different people have different needs, so they need different products (and possibly brands).

Another powerful, yet often overlooked, market research method is the process of understanding one’s market environment. Seriously, if there’s only one thing you could do to learn what works and what doesn’t in your market, you should do a competitive analysis.
“Whenever we discuss building a certain feature, we would definitely research our competitors and see how they do it.”

You’d be surprised by how much you can learn about and from your competition and how much of it can be done online. There are certain tried and tested techniques, hacks, and tools for this type of research, and you can find them in this guide.
Secondary market research data is relatively affordable, fast to acquire, and easy to use. Think market reports, industry insights, and a ton of research data someone has already gathered and analyzed so you don’t have to.
The most reputable sources are Gartner, Forrester, and Pew. Apart from those, make sure to check if there is a trustworthy commercial data source specific to your niche.
Sites like G2, Capterra and Trust Pilot also count. Not only do they give you an overview of your industry, but you can also find some real gems in your users’ reviews and your competitors’ reviews as well. Ahrefs uses that data source regularly internally and externally, like for this section of our Ahrefs vs Semrush vs Moz landing page:

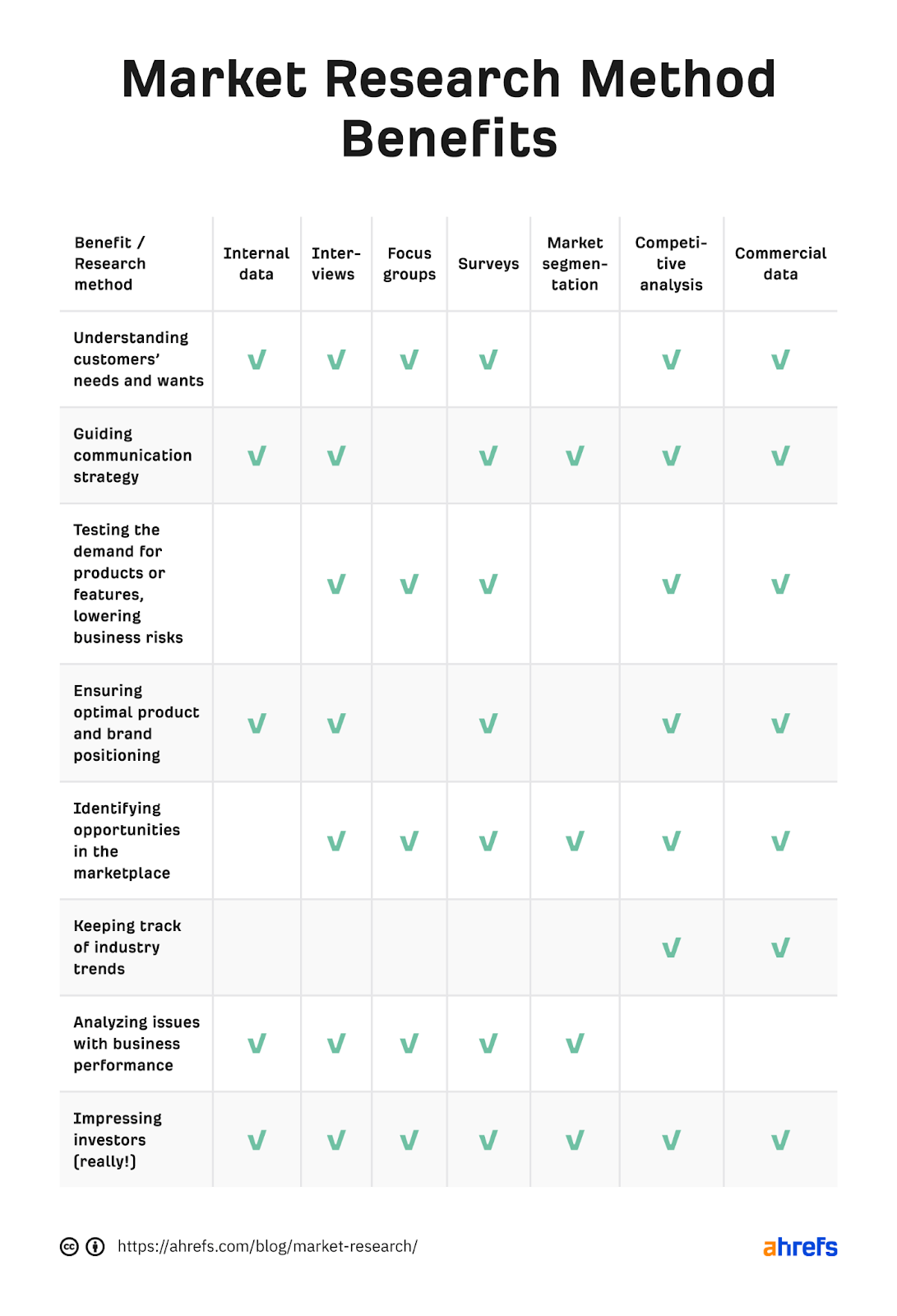
Let’s quickly summarize the above 7 different methods of market research by their key benefits.
So now we know what market research is, why and when to do it, and we’ve learned about all of the important types and methods.
Let’s see how we can use that knowledge to conduct any type of market research in 5 steps. As an example of market research, I’ll tell you about some of my past experiences with a 3D printing company.
This is where every research project starts. You will also find that market research, in general, follows the pattern of the scientific method. First, you need to establish what exactly you are researching.
Do you have a question about your business you want to answer? Maybe you see an opportunity in the market. Or maybe you’ve observed something curious about your product use and you have a hypothesis that you want to validate? State that in the first step of the market research process.
Let me share an example.
In the past, I ran marketing for a few companies, and one of them was a 3D printer manufacturer. Early on I stumbled upon two problems with that company.
First: one of our market segments was saturated with similar products of similar quality at significantly lower price (classic, right?). Second: more and more 3D printing manufacturers seemed to be drifting away from the hobby segment to tackle the professional segments with more expensive products, yet we remained in the hobby/DIY niche. So we were too expensive for hobbyists but too hobbyist for customers who could afford us.
The hypothesis that I wanted to verify was that if the marketplace was showing a trend towards more professional use cases of 3D printing, our company should follow that trend. In other words, I wanted to check the viability of shifting the brand positioning into the professional/premium sector.
We’ve already covered the main types and methods of market research. You should already have a good idea of the differences between primary and secondary research, or whether qualitative or quantitative methods would best suit your needs.
As for the sample of your research, this refers to the portion of the entire data source in question that you will use. For example, if you want to run a survey among your customers, the sample will refer to the selection of customers you will include in your survey. There are a few options for choosing a sample:
Back to our example. As a method for verifying my hypotheses, I chose a mix of:
Once you’ve got your problem, method, and sample nailed, all you need to do is to gather the data. This is the step where you send out your surveys, conduct your interviews, or reach out for industry insights.
A word of advice, choose your market research tool carefully; it will greatly influence the amount of work you will have with analyzing the data. For example, Google Forms automatically makes graphs out of quantifiable data (plus it’s free).
Here’s the data we collected for the 3D printing company:
Now that you have your data collected, the next step is to look for patterns, trends, concepts, or often repeated words—all dependent on whether your method was qualitative or quantitative (or both).
Simple research performed on a small sample will be relatively easy to analyze, or even analyzed automatically, like with the aforementioned Google Forms. Sometimes you will have to use expensive and harder to master software like Tableau, NVivo, PowerBI, or SPSS. Or you can use Python or R for data analysis (if you have a data analyst or data scientist on board, you’re in luck).
Continuing the example: Google Forms made it easy for us to spot patterns in surveys since quantitative data was calculated automatically. The most time-consuming part was reading through all of the responses and manually looking for patterns (back then I wasn’t aware of any tool that could do the job). Both sales and marketing teams worked on analyzing some of the qualitative data to have more than one reference point.
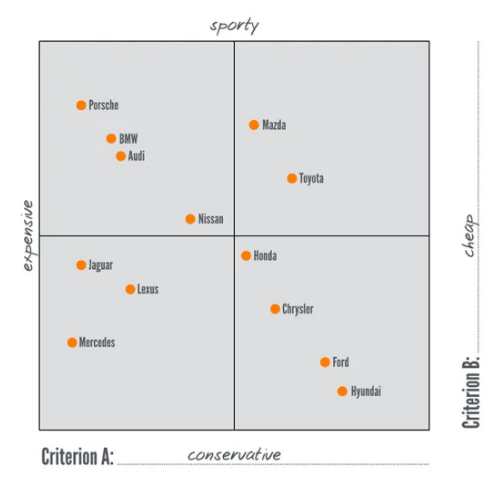
When it comes to researching the competition, coming up with some kind of data structure makes the work more comprehensive (and saner). We put our competitors’ data in specific categories, like products & services (prices included), target market, benefits, values, and brand message. We also used something called a brand positioning map which looks like this:
Analyzing secondary data was probably the easiest part, as the data we needed was already prepared in ready-to-use graphs, statistics and insights. We just had to sift through the contents to look for answers to our questions.
Analyzing the data is not enough. You need to compile your data in a communicative, actionable way for the decision makers. A good practice is to include in your report: all your information, a description of your research process, the results, conclusions, and recommended actions.
Summing up my 3D printing example, I hypothesised that our market was experiencing a major shift and that the company should follow that trend. The research we did verified that hypothesis positively:
Our initial market research lasted for about two months. We also came back to it whenever we had the chance (or the necessity) and reiterated it to see if we were on the right track.
Was it worth it? Let me tell you this: it saved the company. Our research showed us that this was the last call to reposition the brand and the product. Our original target segment was being gradually dominated by companies we couldn’t compete with.
It took us some time to get buy-in from key stakeholders and implement the conclusions throughout the whole company (eventually, we got it right). As a result, we increased sales, increased customer satisfaction and put ourselves on a more profitable growth track—a win-win for everyone. We even went as far as merging with another manufacturer to shorten the time to get to that sweet market spot.
Looking back, no one from our close competitors survived. They didn’t adapt as we did, and we owed everything to market research.
Whatever you do, avoid these common market research mistakes:
Market research reaches back to the 1930s and it’s probably rooted even “deeper” than the 20th century. Everything you could do then you can do now better, faster and cheaper thanks to these online tools and resources.
I’ve put together 3 quick wins that can help with your market research—and that’s only a taste of what you can do with Ahrefs.
In the early 20th century, you’d have to hire market researchers to spend days or even weeks asking people “have you heard about brand X”. Today, you can simply look up the search volume for that brand.
So let’s say you run a drone manufacturing brand, and you want to check out your competitors’ brand awareness in France. Go to Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, input the names of the brands, select “France” as your market, and in a flash you get:
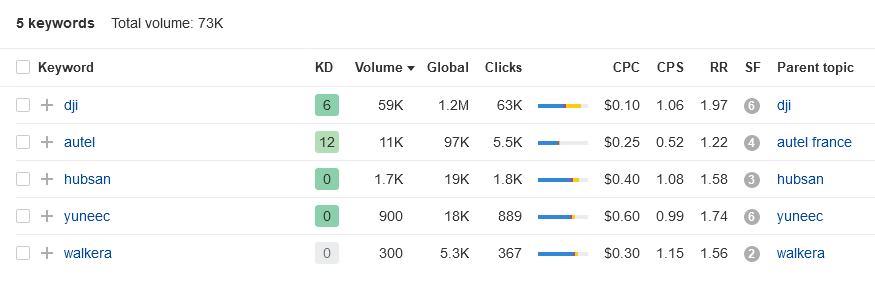
The branded keyword volume indicates the brand awareness of that brand in a particular market. You can also keep track of that data by performing this search regularly to see if there are significant changes over time (for example, impacted by a recent campaign).
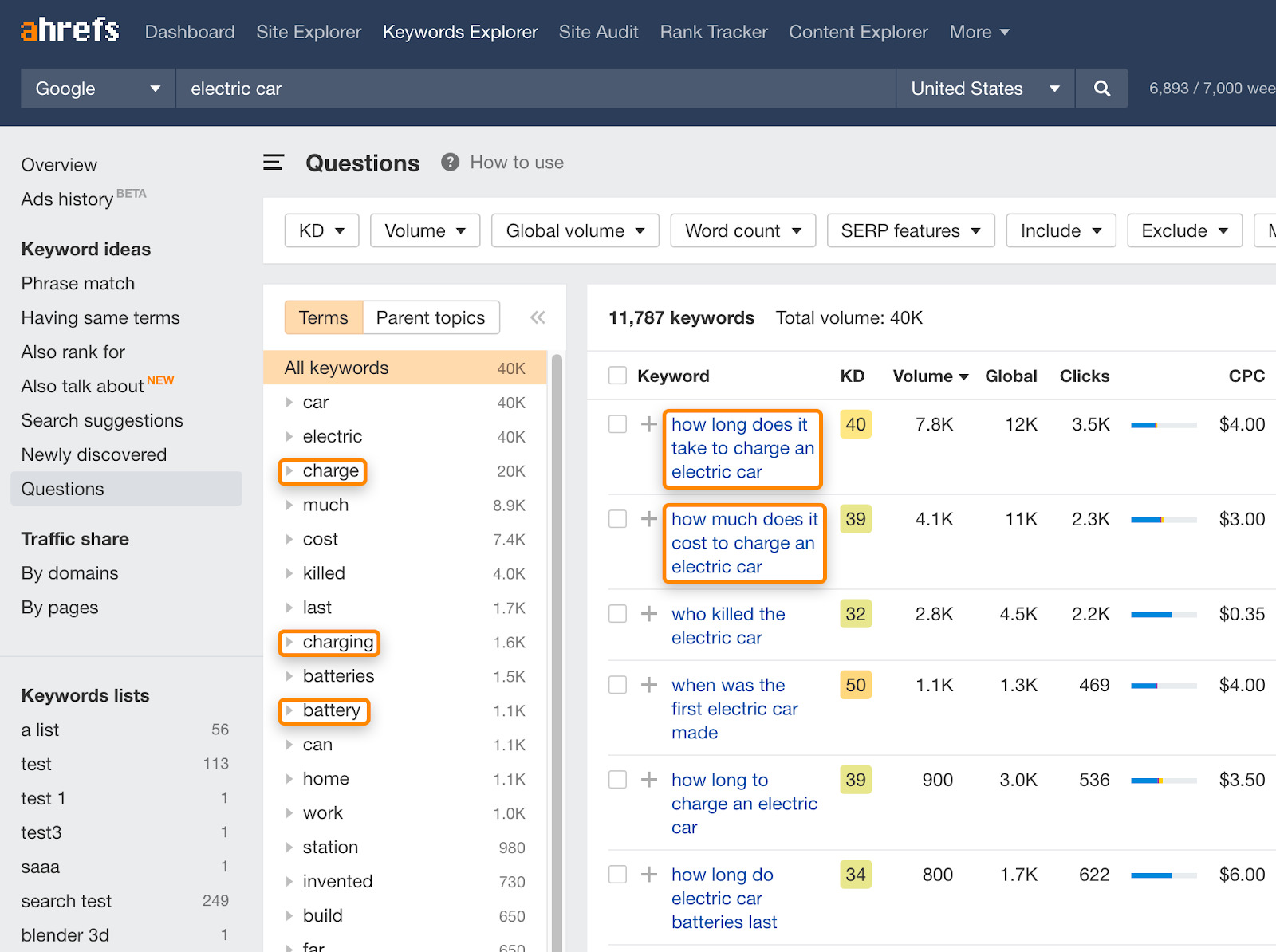
The next game-changing feature for electric cars will concern batteries, charging time, and charging cost (and not autopilot). How do I know?
Well, I opened Ahrefs Keywords Explorer, typed in “electric cars”, and went to the Questions report to find out what people search for. This gave me an idea of what problems electric car owners have (and potential owners worry about). You can easily perform similar research for your niche.
Gerald Zaltman in his popular book “How Customers Think” proposes the idea that one of the major erroneous assumptions of marketing is that consumers think in words.
On the other hand, when consumers Google something they have to think in words. And when we market to those consumers we have to think in words as well. The question is: which words?
Let’s say that you want to enter a new and innovative market in the USA, for example the synthetic fermentation-derived dairy industry, also called animal-free dairy.
To you, this set of words “animal-free dairy” may be the very center of your business and marketing efforts. But let’s see what other people think. Let’s use Keywords Explorer to see how many people search Google in the U.S. just for that phrase:
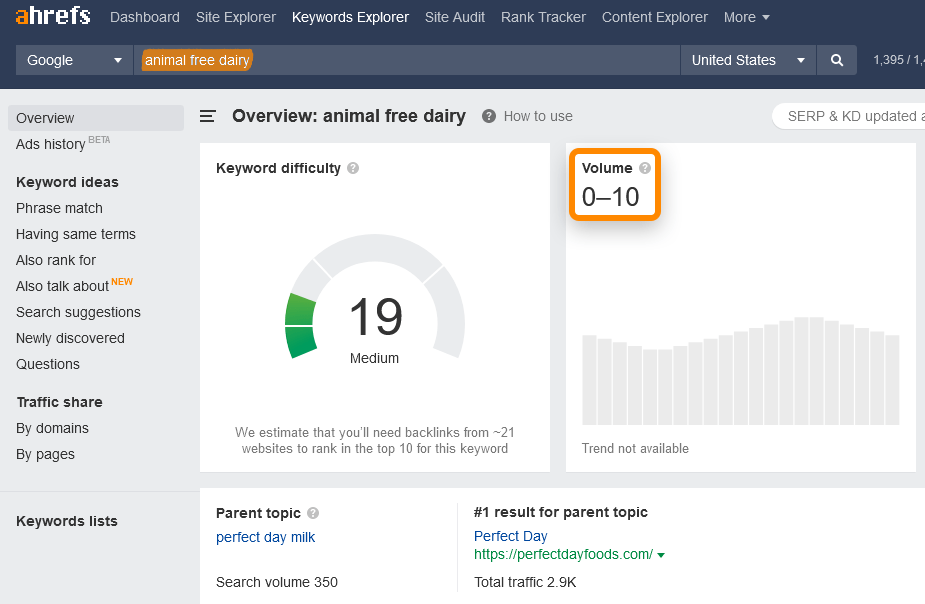
Whoops! Looks like your product category has disappointingly low awareness. Does this mean you’re doomed? Not necessarily.
Let’s try other words. Words that mean something different, but still closely related to your new product.
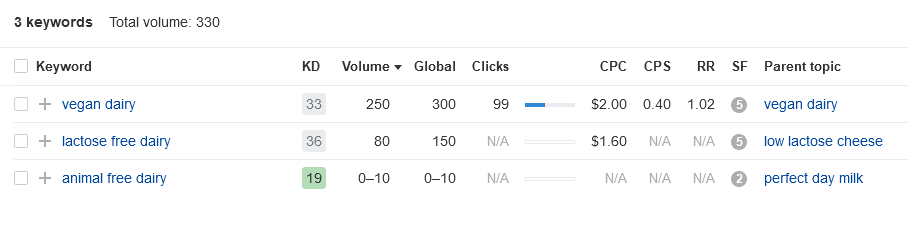
Now we’re onto something. People search for “vegan dairy” and “lactose free dairy” more often. Not the same, but closely related. Yet, look at the difference in search volume.
Words make a huge difference. And Google knows that.
The only reason you were able to put all of those three phrases in the same bucket was that you knew the connection between those words. The problem is that your target audience may not know that connection; they may not even know that this kind of product exists. This quick analysis of search volume shows that you may want to make that connection, for example with content marketing.
If you create content around related higher volume keywords, you can potentially get more organic traffic than simply focusing on the keyword designating your product category. Look, even though you might believe the main benefit of your animal-free product is something unrelated to lactose, e.g., cruelty-free production, you might want to address the problem of lactose intolerance to appeal to people with this condition.
But that’s not all. You may have noticed “low lactose cheese” in the bottom right corner. This refers to the nifty feature of Ahrefs’ Keyword Explorer called “Parent topic”. Parent topic indicates that Google sees a given keyword as part of a broader topic.
If we click on this Parent topic, we uncover even more search demand:
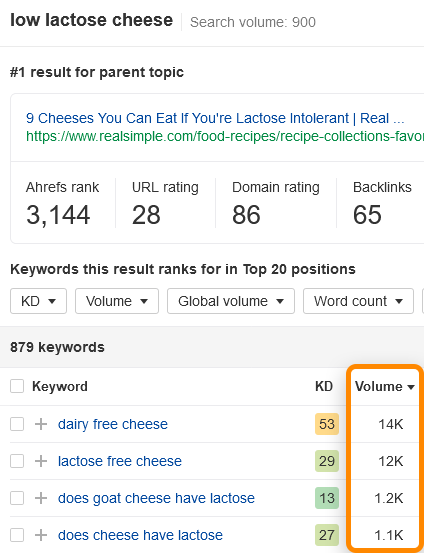
We can see that the search for the topic “low lactose cheese” exceeds the “vegan dairy” topic by almost 300% in the US. Also, uncovering that parent topic gave us 879 potential keyword ideas (some of them have even higher search volume, like “lactose free cheese”).
Want to discover even more topic associations? No problem. You can dive deeper into this research by using other features of Ahrefs’ Keyword explorer. For example,the Also rank for report allows you to see which other keywords (and topics) the top 100 ranking pages for your target keyword also rank for.
This market research quick-win ties into the broader topic of keyword research. If you want to uncover even more keyword ideas and learn how to analyze them, read our keyword research guide.
Customer Relationship Management software is used to manage and track interactions between a company and its customers and prospects. Usually, it works in tandem with sales or marketing automation software (or has integrations for them). If used properly, it is a true cornucopia of market insight.
As I pointed out earlier, it’s one of those primary data sources that you can leverage to discover patterns in your customer behaviour or characteristics. Popular choices are Hubspot, Salesforce, Intercom, but there is a ton of CRM software out there, so check out a software comparison like G2 to see what best suits your needs.

This type of tool allows you to carry out our aforementioned survey research method online.
Create targeted, user-specific surveys and analyze answers with tools like Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, Typeform, or Qualaroo.
Sending out your typical email with a survey is not the only option, for example with Qualaroo you can display surveys:
Need more? No problem, check out SurveyMonkey’s Market Research solution. It taps into the agile market research models we’ve discussed. They’ve got 14 online solutions that help you stay on top of your game, including customer segmentation, monitoring market dynamics, brand, creative analysis, feature importance, finding the right price for your products, and more.
So you think you have a tough business challenge? This daring gentleman is trying to disrupt… eggs. Extremely hard, but doable with market research on his side.
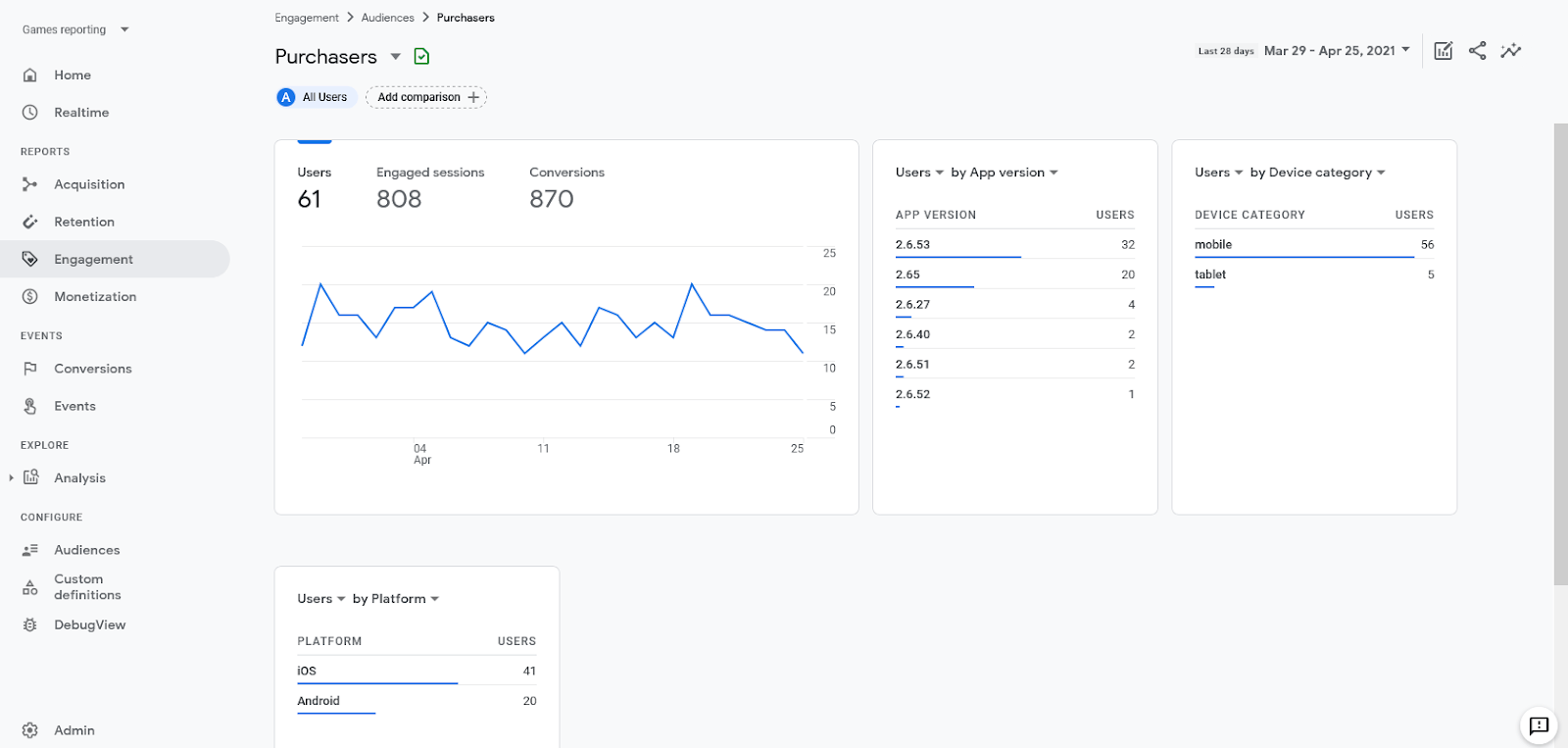
Tracking your website or app traffic is absolute marketing basics. Just look at some data dimensions Google Analytics offers:
Sounds familiar? Yup, that sounds like good ol’ market segmentation. Here’s the best part: it’s free, quick to perform and it’s based on your primary data.
If you’ve never dug deeper into Google Analytics, or similar analytics software (e.g., Matomo, Woopra) here are some questions that this marketing technology can answer for you:
If you’re already using Google Analytics, see if you’re not making these Google Analytics tracking mistakes.
Commonly used by UX designers, but just listen to the value propositions of these tools:
Again, sounds much like our market research methods, right? And it’s no joke, thousands of companies use these tools.
User experience research tools allow you to get user feedback and insights on your products, prototypes, websites, and apps.
Testing is based on tasks your test-takers perform. You can either use your own user base or define a custom base using their services. You’ll get written reports and even recorded videos that you can incorporate into your market research and make sure you’re properly taking advantage of that market opportunity.
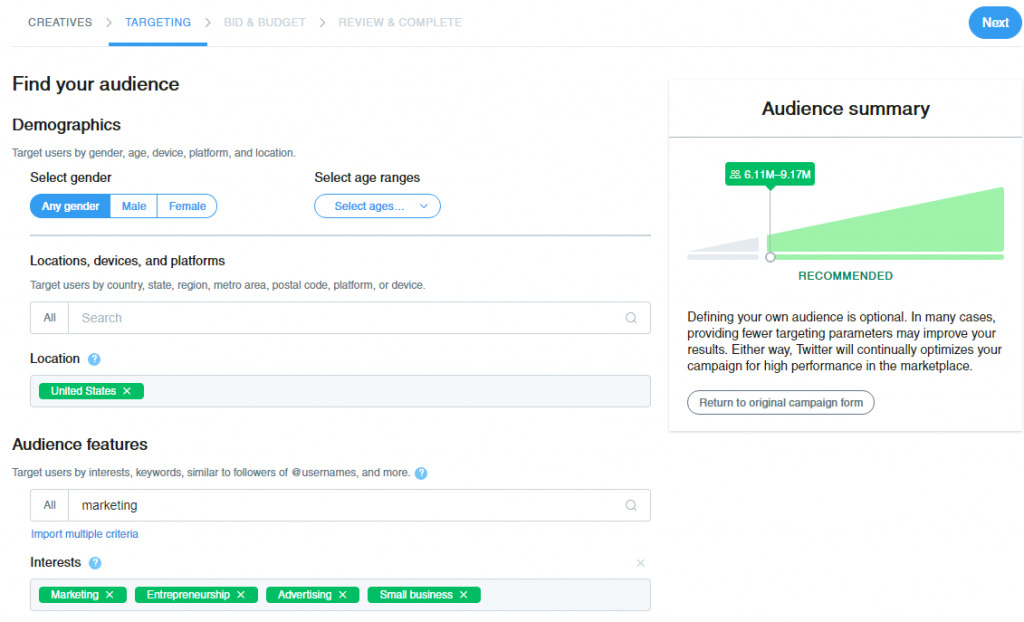
That’s right—the Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter ad planner you already use for running ads can give you some insight into the numbers behind the market segments you’re interested in.
30+ males with higher education interested in technology gadgets? No problem. Female C-suite decision-makers from Europe? It’s all there.
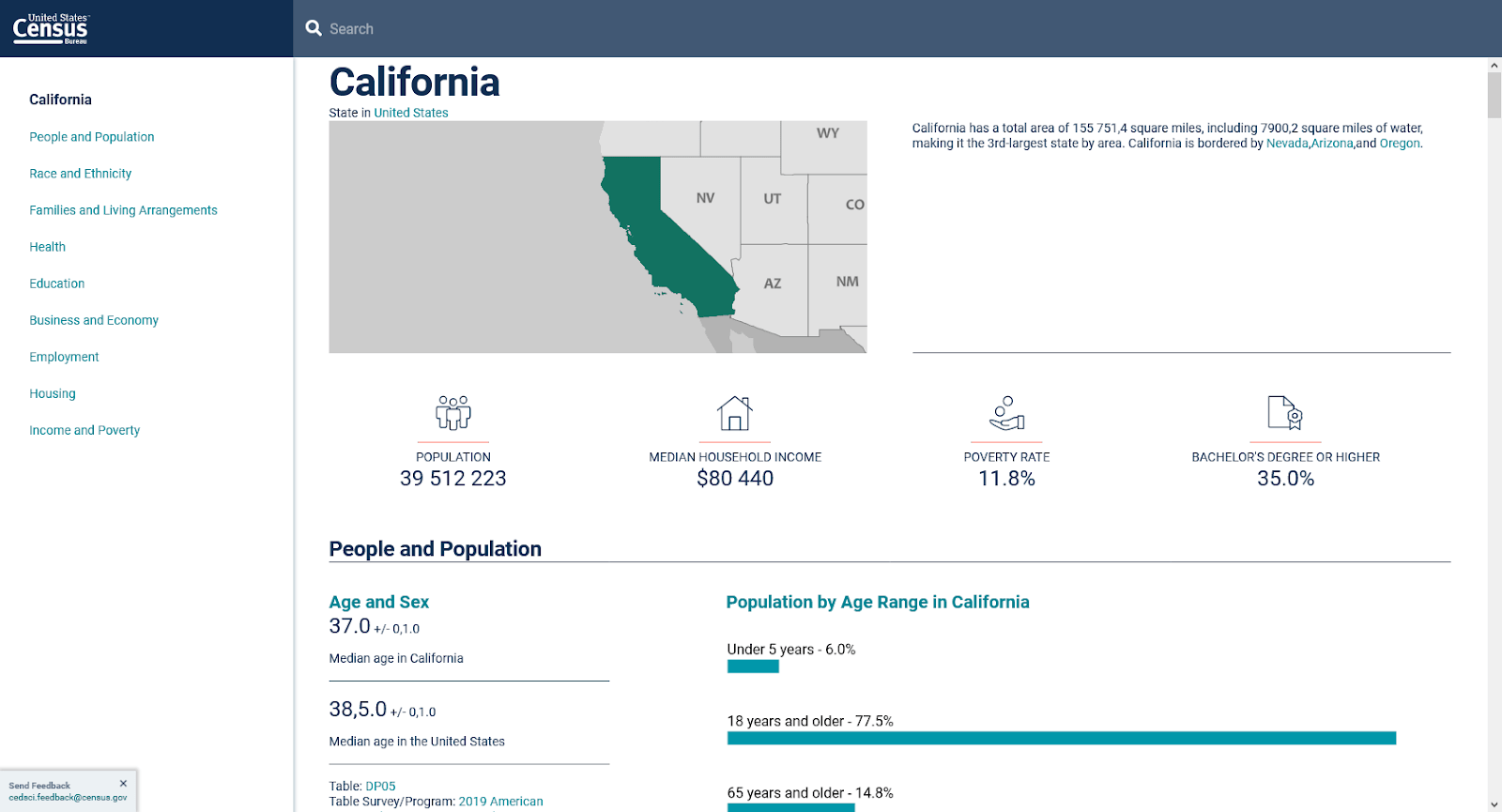
The availability of this kind of data may vary based on your target market. For example, in the US the Census Bureau offers a free resource for searching the country’s census data. You can filter the data by topics, years, geography, surveys, or industry codes. You can also access premade interactive tables (which you can also download) or simply explore certain regions of the country using their maps.
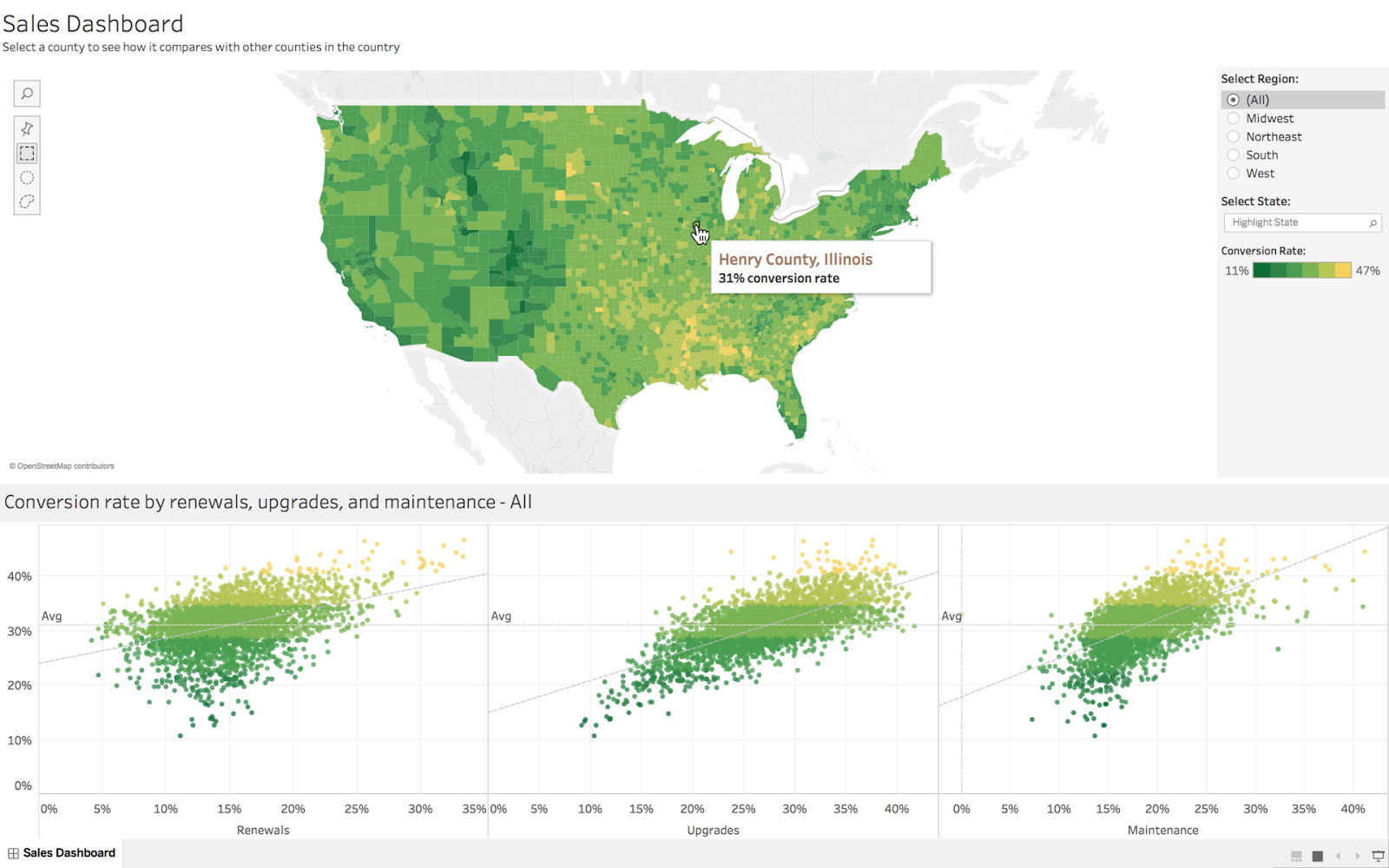
With business intelligence tools like Tableau, Looker or Sisense, you can connect to any data source to perform data cleaning, statistical operations, and data visualization. They are designed to allow you to glean insights into your data, and communicate effectively with your stakeholders. It’s like SQL combined with R, but you don’t need coding skills and you get a user-friendly interface.
Because these tools are overflowing with functionality and because they are usually pricey, they are overkill for small companies with basic market research needs. Often you will find that the tool that you are already using for your research method comes with some data analysis and visualization functions. And if not, you can always import your data to Excel or Google Docs and use Google Data Studio for a shareable interactive presentation.
Market research is no easy feat. If you feel intimidated by it, you’re not the only one. But don’t shy away from it. The benefits of conducting even sporadic market research can have benefits for your business you simply can’t ignore. You won’t turn into a market research pro overnight, but the good news is you don’t have to. You can go the agile way (like Ahrefs), use affordable self-service online tools and resources, or you can even outsource your research. As long as you base your marketing game plan on valid data, you dramatically improve your chances for success.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter.